Remote Environment in Business Definition
This article provides complete information about the elements/components of business environment!
The business environmental factors may be classified into different types. There are broadly two types of environment that affects the organisation, internal environment and external environment.

Image Courtesy: privatesectordevelopment.se
Inland Environment :
Environment which lies within the origin is known as internal environment. Internal factors are generally regarded as controllable factors.
Factors of Internal Environment : 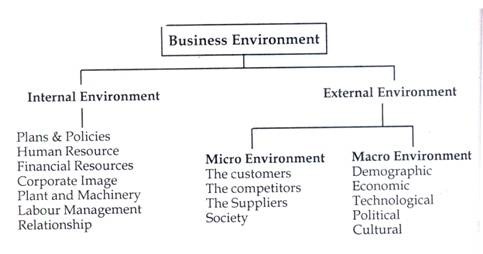
Internal environment includes internal factors of the business. It includes plans and policies, human resource, financial resource, corporate image, plant and machinery, labour-management relationship, promoter's vision etc. The components of internal environment are controllable.
The following are the factors of internal environment:
1. Plans & Policies:
The plans and policies of the firm should be properly framed taking into consideration the objectives and resources of the firm. Proper plans and policies help the firm to accomplish its objectives.
The higher authority must analyse the internal environment to foresee the changes and frame appropriate policies well in time.
For example: the personnel policy in respect of promotion should be based on merit rather than seniority.
2. Human Resource:
The survival and success of the firm largely depends on the quality of human resources. The social behaviour of the employees greatly affects the working of the business. The characteristics of human resource like skill, quality, morale, commitment can contribute to the success of the organisation.
If the employees of the organisation are skillful and committed, it can take the firm to a great height. Neglecting the human resource by the management can hamper the success of the organisation.
3. Financial Resources :
Capital is the lifeblood of every business. Finance relates to money. A firm needs adequate funds to meet its working capital and fixed capital requirements. There is a need to have proper management of working capital and fixed capital.
Financial factors like financial policies, financial status (position) and capital structure 'a/so influence the internal environment of a firm affecting its performance- If the firm enjoys sufficient financial resource, it can spend on research and promotional activities.
4. Corporate Image :
A firm should develop, maintain and enhance a good corporate image in the minds of employees, investors, customers etc. Poor corporate image is a weakness of the firm.
Constant research and development activities should be undertaken by the firm to enhance the quality of the brand. This helps in creating a corporate image and strengthens the standard of the firm in the market.
5. Plant and Machinery :
Plant and machinery is the internal part of the business firm. If the machines are obsolete or outdated, they should be replaced by a new one, or that adversely affects the business firm.
6. Labour and Management Relationship :
There should be smooth labour and management relationship. The management should understand the problems of their workers and gain confidence in them. The labours should be motivated by providing with monetary and non-monetary incentives (benefits).
Better Labour- Management relationship helps in increasing the morale of the employees and motivates them to put efforts in the business. Such strong relationship enhances organisations development.
7. Promoters vision :
The promoter should have far sight vision to forecast opportunities and threats in the business so that the opportunities are properly grabbed and threats are diffused off in time.
External Environment :
To run the business successfully, it is necessary to understand the environment with in which the business operates. Business environment j is a set of external factors that affects the business decisions.
The environment, which lies outside the organisation, is known as external | environment. External factors are unpredictable and uncontrollable. They are beyond the control of the company.
Definition of external environment:
According to William Glueck and Jauck, "In environment there are several factors which constantly bring opportunities and threats to the business firm. It includes social, economic, technological and political conditions".
External environment is further classified as:
I. Micro Environment
II. Macro Environment
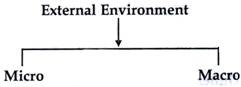
I. Micro Environment :
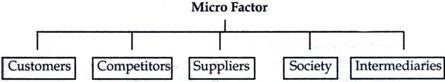
Micro environment is also known as operating environment. It consists' of company's immediate environment that affect its performance. It includes customers, suppliers, intermediaries, competitors etc. The micro environment consist the elements that directly affects the company.
According to Philip Kotler, "Micro environment consist of the factors in the company's immediate environment which affects the performance of the business unit. These include suppliers, market intermediaries, competitors, customers and the public".
1. The customers :
Consumer is the king of the market. They are the centers of the business. They are one of the most important factors in the external environment. Customer satisfaction has become more challenging due to globalisation.
Nowadays, consumer expectations are high. Therefore the firm must keep in mind the customer's expectations, their requirements and accordingly make market decisions. The success of the business depends upon identifying the needs, wants, likes and dislikes of the customers and meeting with their satisfaction.
Businesses have different classes of customers like wholesale customers, retail customers, industrial customer's foreign customers etc. To enhance growth, it is necessary for the business firm to identify the needs of these customers and should undertake research and developmental activities.
2. The competitors :
The company has to identify its competitor's activities. Information must be collected about competitors in respect of their prices, products, and promotion and distribution strategies. World is becoming a global market.
Business firm has to face tremendous competition not only from Indian business firm but also from foreign firms. To achieve growth and success they have to monitor various activities of their competitors.
Liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation have promoted competition that has created threats to domestic units. The business must understand the strategies framed by the competitors to respond in an effective manner.
3. The Suppliers :
Suppliers supply raw material, machines, equipment's and other supplies. The company has to keep a watch over prices and quality of materials and machines supplied. It also has to maintain good relations with the suppliers.
It is necessary to have reliable source of supply for the smooth working of the firm. Uncertain supplies compel the firm to maintain high inventories resulting into increase in the cost. The business should not only rely on the single supplier but also have relations with multiple suppliers.
4. Society :
Society affects company's decisions. The expectation of the society from the business is increasing. Therefore the business firm maintains public relations department to handle complaints, grievances and suggestions from general public. The members of the society include:
i. Financial institutions
ii. Shareholders
iii. Government
iv. Employees
v. General public
5. Marketing intermediaries:
Market intermediaries include agents and brokers who help the business firm to find the customers. They help the firm to promote and distribute the goods to the final consumers.
They are the link between the firm and the final customers. Market intermediaries include wholesalers, retailers, advertising firm, media, transport agencies, banks, financial institutions etc. They assist the company in promoting and targeting its product to the right market.
II. Macro Environment :
The macro environment consists of the larger societal factors that affect the working of a firm. Macro environment is also known as general environment. The macro factors are generally uncontrollable.
The macro environment factors are briefly discussed as follows:
Definition of Macro Environment:
According to Philip Kotler, "Macro environment create forces that creates opportunities and pose threats to the business unit. It includes economic, demographic, natural, technological, political, political and cultural environments."
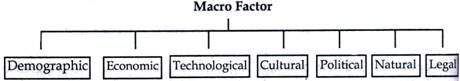
Macro Factor:
Demographic Economic Technological Cultural Political Natural Legal
1. Demographic Environment :
Demographic Environment relates to the human population with reference to its size, education, sex ratio, age, occupation, income, status etc. Business deals with people so they have to study in detail the various components of demographic environment.
Demographic environment differs from country to country. Demographic factors like size of the population, age composition, density of population, rural-urban distribution, family size, income level, status etc. have significant implications on business.
For example: If the population is large, then the demand for goods and services will be more. It will have favourable effect on the business. In the same way educational level is also an important factor affecting business.
2. Economic Environment :
i. Economic environment consists of economic factors that influence the functioning of a business unit. These factors include economic system, economic policies, trade cycle, economic resources, gross national product, corporate profits, inflation rate, employment, balance of payments, interest rates, consumer income etc. Economic environment is dynamic and complex in nature
A business firm closely interacts with economic environment that consist of:
a. Economic conditions in the market i.e. demand and supply factors
b. Economic policies of the government: monetary policy, fiscal policy, industrial policy, trade policy, foreign investment policy etc.
ii. Economic system prevailing in the country also affects the business growth. Every country has different economic system. The economic system includes capitalism, socialism, and mixed economy. Business depends upon economic environment for their inputs and also for market. Changes in the economic factors can adversely affect the working of a business firm.
3. Technological Environment :
Technology has brought about far reaching changes in the methods of production, quality of goods, productivity, and packaging. There is a constant technological development-taking place.
The business firm must constantly monitor the changes in the technological environment, which may have a considerable impact on the working of a business. It also indicates the pace of research and development and progress made in introducing modern technology in production.
Technology provides capital intensive but cost effective alternative to traditional labour-intensive methods. In a competitive business environment technology is the key to development. Technology helps to run the business better and faster.
4. Cultural Environment :
Culture involves knowledge, values, belief, morals, laws, customs, traditions etc. Culture passes from one generation to another through institutions like family, schools, and colleges. Business is an integral part of the social system.
Society is largely influenced by the culture and in turn culture influence the business firm. Culture shapes the attitude and behaviour of the society. Any change in the cultural factor affects the business in large. Business should be organised and governed, taking into consideration various values and norms of the society.
5. Political Environment :
The political environment in a country influences the legislations and government rules and regulations under which a firm operates.
Political environment means influence exerted by:
a. Legislature:
This includes parliament, legislative assemblies. They are the law making bodies that frame rules and regulations.
b. Executives:
They include government beurocracy who implements the decision.
c. The Judiciary:
It includes Supreme Court, High Court who sees whether the decisions taken and implemented by the executive are within the constitutional framework. They are also known as dispute settlement bodies.
Legislature, executives and judiciary are the important pillars of political environment. A stable progressive and healthy political environment is very necessary for the growth and development of business.
6. Natural Environment :
Resource availability like land, water and mineral is the fundamental factor in the development of business organisation. It includes natural resources, weather, climatic conditions, port facilities, topographical factors such as soil, sea, rivers, rainfall etc.
Every business unit must look for these factors before choosing the location for their business.
The natural environment largely determines the functioning of a business firm. Natural environment has a great influence on the working of a business. The business organisation should consider the natural factors before starting their operations.
Natural calamities like flood, drought, cyclone, Tsunami etc. can also affect the business environment.
7. Legal Environment :
The state sets the formal rules, laws and regulations for the country's operational system. It creates a framework of rules and regulations within which a business has to operate. The business should have complete knowledge of laws and policies to run the business effectively. Some of the laws are:
a. Consumer protection Act-1986
b. Factories Act-1948
c. Workers compensation Act-1923
d. FEMA Act-1999
e. The Companies Act-1956
f. The Environment protection Act-1986
Remote Environment in Business Definition
Source: https://www.businessmanagementideas.com/business-environment/business-environment-the-elements-of-business-environment-1968-words/507
0 Response to "Remote Environment in Business Definition"
Post a Comment